New Delhi, September 28: As World Heart Day approaches on September 29, the World Heart Federation is encouraging global citizens to prioritize their heart health. One digital companion in this endeavor is the Apple Watch, renowned for alerting users to potential signs of atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Apple Watch Series 9, alongside previous models, discreetly monitors users’ heart rates for any irregularities, whether unusually high or low, which can be indicative of underlying health issues. This feature aids users in identifying situations that might necessitate further medical evaluation.
If an Apple Watch wearer’s heart rate exceeds 120 beats per minute (bpm) or drops below 40 bpm while appearing sedentary for 10 minutes, the device triggers a notification. Users have the flexibility to customize these thresholds or toggle the notifications on or off. All heart rate notifications, including date, time, and heart rate data, can be conveniently accessed through the Health app on their iPhone.
The watch also boasts an irregular rhythm notification feature, which periodically assesses the wearer’s heartbeat for irregularities that may suggest AFib. AFib is a type of irregular heart rhythm where the upper and lower chambers of the heart beat out of sync. Some individuals with AFib may not experience noticeable symptoms, while others might encounter rapid heartbeat, palpitations, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
The irregular rhythm notifications leverage the optical heart sensor on the Apple Watch to detect pulse wave variability in resting users. If the algorithm repeatedly detects an irregular rhythm indicative of AFib, the user receives a notification, and the relevant data, including date, time, and beat-to-beat heart rate, is logged in the Health app.
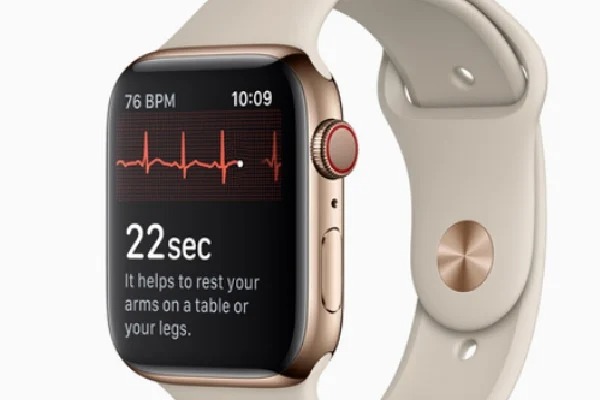
For users experiencing symptoms like rapid or irregular heartbeats, the ECG app on the Apple Watch allows them to capture an electrocardiogram (ECG) and document their symptoms. This app utilizes the electrical heart sensor within the Digital Crown and the back crystal to record a single-lead ECG. It then provides results, such as sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, atrial fibrillation with a high heart rate, inconclusive, or poor recording, and prompts users to input additional symptoms like dizziness or fatigue. Users can export the recorded data as a PDF from the Health app for sharing with healthcare professionals.
The Cardio Fitness feature offers an estimate of VO2 Max, an indicator of the body’s ability to absorb oxygen during exercise. This is recognized by heart health experts as a crucial predictor of overall health, and Apple Watch provides users with a scientifically validated estimate of VO2 Max. Users can even choose to receive notifications if their classification drops to “low,” indicating a higher risk of long-term health conditions. Fortunately, this can be improved through regular exercise, which users can easily monitor and track.
AFib History on the Apple Watch provides an estimate of the time your heart displays signs of AFib. This information is vital, as research has shown that the duration of AFib can relate to symptom severity, quality of life, and the risk of complications. Users can also monitor factors like sleep, exercise, and weight that may influence their AFib duration, offering valuable insights.
Traditionally, tracking AFib over time and comparing it to lifestyle factors has been challenging. However, wearing an Apple Watch simplifies this process, providing users with a comprehensive overview of their heart health and its connections to their daily life.